Benchmark Maps: A Basis for Spatial Evaluation and Resolution-Making
Associated Articles: Benchmark Maps: A Basis for Spatial Evaluation and Resolution-Making
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Benchmark Maps: A Basis for Spatial Evaluation and Resolution-Making. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Benchmark Maps: A Basis for Spatial Evaluation and Resolution-Making
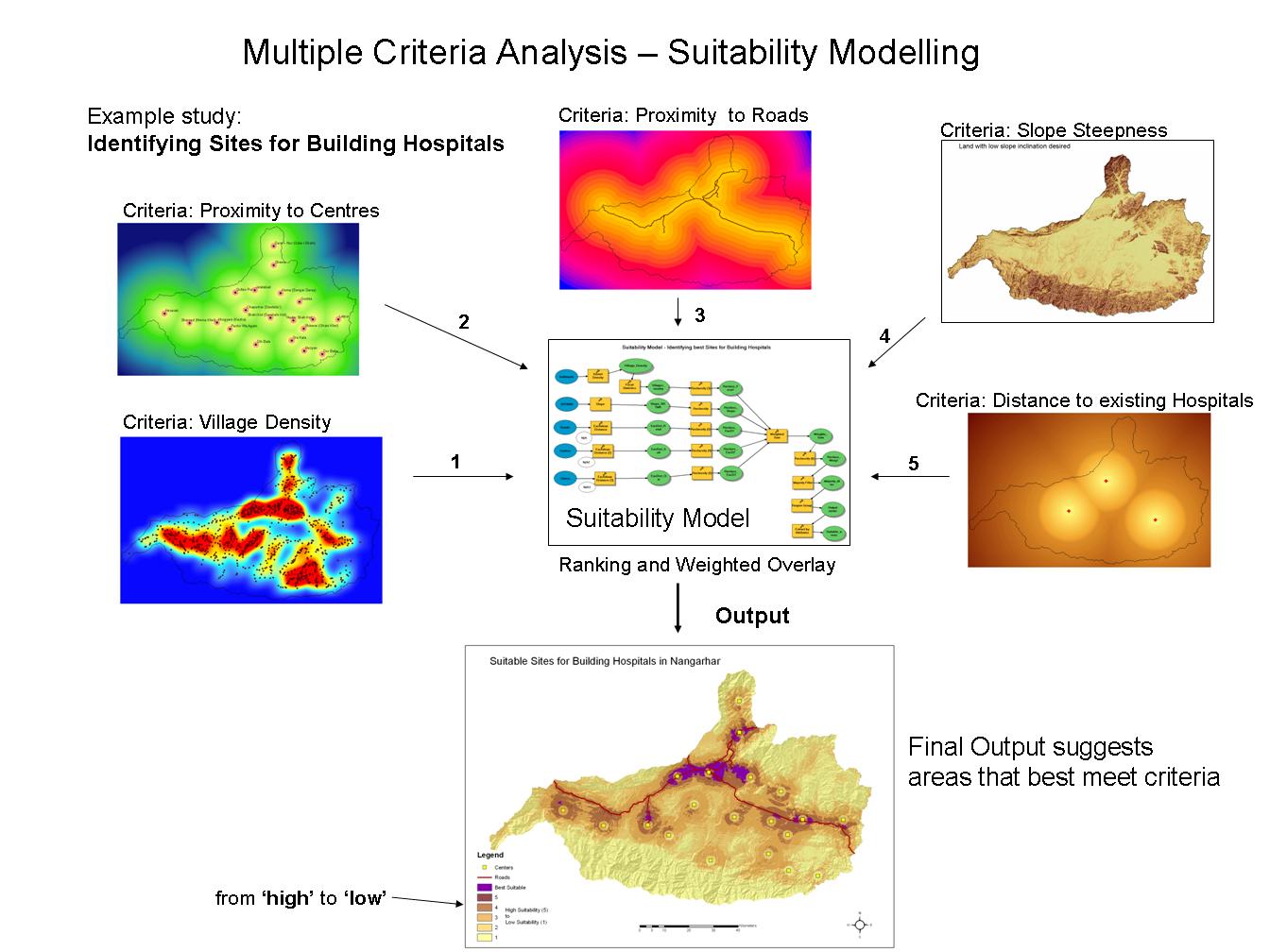
Benchmark maps, also called base maps or reference maps, function elementary instruments in varied fields, from city planning and environmental administration to geographic data techniques (GIS) and cartography. They supply a foundational spatial framework, a standard reference layer upon which different geographic information may be overlaid and analyzed. In contrast to thematic maps that spotlight particular options or phenomena, benchmark maps prioritize correct illustration of geographic location and important spatial options, forming the bedrock for spatial understanding and knowledgeable decision-making.
This text delves into the essential function of benchmark maps, exploring their parts, development strategies, functions, and the challenges concerned of their creation and upkeep.
Elements of a Benchmark Map:
A complete benchmark map sometimes features a vary of important parts, working collectively to offer an entire and correct illustration of the geographic space. These parts embrace:
-
Geographic Coordinates: The inspiration of any map is its coordinate system. This might be latitude and longitude (geographic coordinates) or a projected coordinate system (e.g., UTM, State Aircraft) tailor-made to the precise space. Correct coordinate referencing ensures exact location of all options.
-
Scale: The size defines the connection between distances on the map and corresponding distances on the bottom. Selecting an acceptable scale is crucial; a large-scale map reveals a smaller space in larger element, whereas a small-scale map reveals a bigger space with much less element.
-
Map Projection: As a result of the Earth is a sphere, representing its floor on a flat map necessitates a projection. Varied map projections exist, every with its strengths and weaknesses regarding distortion of space, form, distance, and course. The selection of projection relies on the map’s function and the world being mapped.
-
Geographic Options: That is the core of the benchmark map, encompassing a variety of pure and human-made options. These embrace:
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, streams, oceans, and different water our bodies.
- Topography: Elevation, terrain, slopes, and hills. That is typically represented utilizing contour strains, digital elevation fashions (DEMs), or shaded reduction.
- Transportation Networks: Roads, railways, airports, and waterways.
- Political Boundaries: Nations, states, provinces, counties, and municipalities.
- Constructed Atmosphere: Buildings, buildings, and concrete areas.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and different vegetation sorts.
-
Map Legend: A key factor explaining the symbols, colours, and patterns used on the map to symbolize completely different options. A transparent and concise legend is essential for map interpretation.
-
**Map


![What is Spatial Analysis? [Explained]](https://gisnavigator.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/GIS-Body-Images-Importance-of-Spatial-Analysis.webp)




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Benchmark Maps: A Basis for Spatial Evaluation and Resolution-Making. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!