Decoding the ASHRAE Local weather Zones Map: A Complete Information to Local weather Classification
Associated Articles: Decoding the ASHRAE Local weather Zones Map: A Complete Information to Local weather Classification
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the ASHRAE Local weather Zones Map: A Complete Information to Local weather Classification. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the ASHRAE Local weather Zones Map: A Complete Information to Local weather Classification

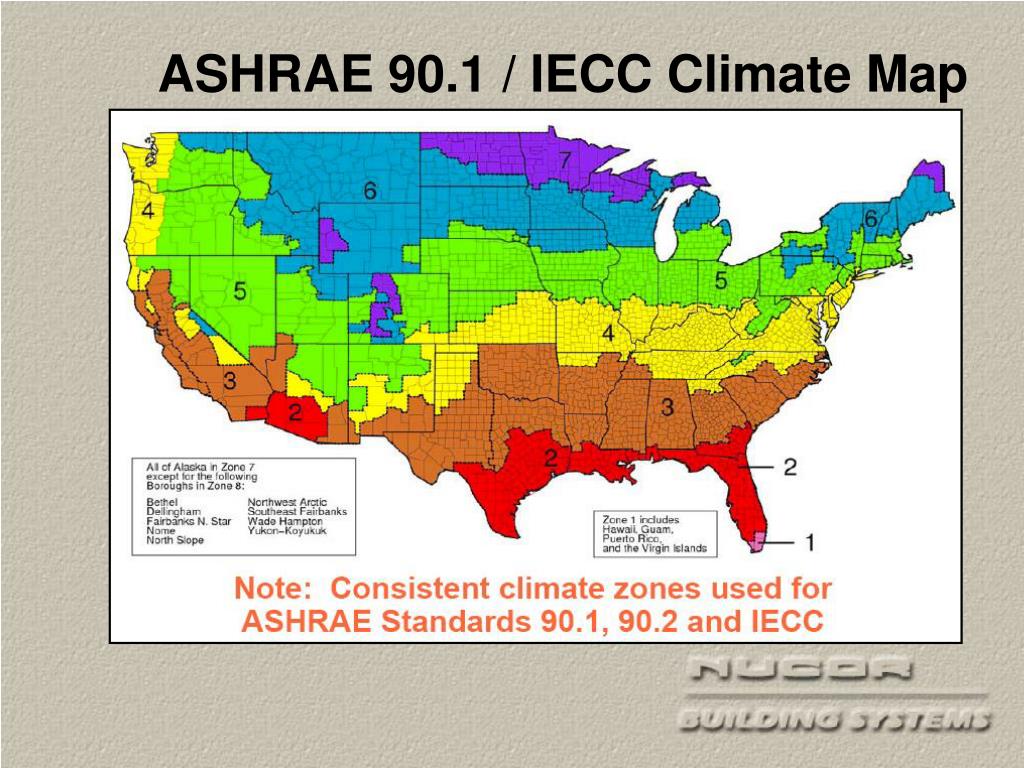
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) Local weather Zones map is a elementary device for architects, engineers, builders, and anybody concerned within the design and building of buildings. This map, based mostly on meticulously collected climate knowledge, classifies areas throughout the globe into distinct local weather zones, every characterised by particular temperature and humidity ranges. Understanding these zones is essential for designing energy-efficient and comfy buildings tailor-made to their particular climatic context. This text delves into the intricacies of the ASHRAE local weather zones map, its methodology, its purposes, and its evolving position in sustainable constructing design.
The Evolution of ASHRAE Local weather Zones:
The ASHRAE local weather classification system has undergone a number of revisions, reflecting developments in local weather science and the rising emphasis on vitality effectivity. Early variations targeted totally on heating and cooling diploma days, less complicated metrics that mirrored the vitality demand for heating and cooling. Nevertheless, as local weather change intensified and vitality conservation turned paramount, the necessity for a extra nuanced system turned obvious. The present system, primarily represented by the 2013 model (ASHRAE Normal 169), incorporates extra subtle parameters, providing a extra granular and correct illustration of weather conditions.
Methodology and Parameters:
The ASHRAE local weather zones aren’t arbitrarily outlined. The methodology includes analyzing historic climate knowledge, particularly specializing in key parameters that considerably affect constructing vitality efficiency:
- Dry-bulb temperature: That is the air temperature measured by a typical thermometer, representing the air’s wise warmth. It’s a essential think about figuring out heating and cooling masses.
- Moist-bulb temperature: This temperature accounts for each the wise warmth and the latent warmth (moisture content material) of the air. It’s important for understanding humidity ranges and their influence on human consolation and constructing vitality wants.
- Humidity: Relative humidity, expressed as a share, signifies the quantity of moisture within the air in comparison with the utmost quantity it will probably maintain at a given temperature. Excessive humidity will increase cooling masses and might influence indoor air high quality.
- Photo voltaic radiation: The quantity of photo voltaic vitality obtained at a location considerably impacts constructing heating and cooling wants. This issue varies based mostly on latitude, altitude, and cloud cowl.
- Wind velocity and route: Wind impacts constructing warmth loss and achieve, influencing the design of constructing envelopes and pure air flow methods.
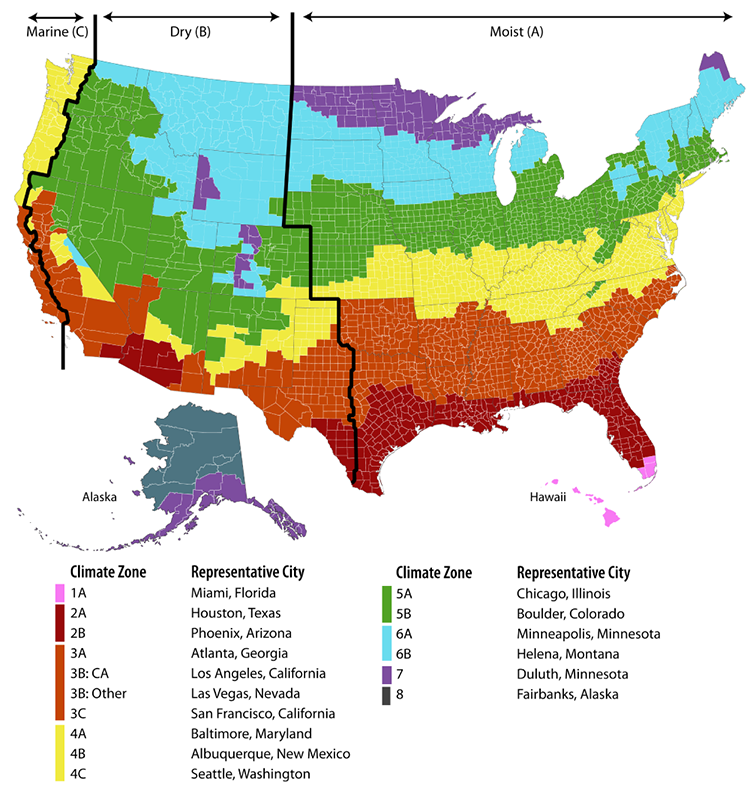
These parameters are analyzed utilizing subtle algorithms to generate the local weather zone designations. The ensuing map divides areas into varied zones, sometimes denoted by numbers (e.g., Zone 1, Zone 2, and so on.) and generally additional subdivided by letters (e.g., 3A, 3B) to mirror delicate variations inside a broader zone.
Understanding the Zone Classifications:
The ASHRAE local weather zones aren’t merely about temperature ranges; they symbolize the interaction of a number of climatic components. A better zone quantity usually signifies a warmer and/or extra humid local weather, requiring extra important cooling masses. Decrease zone numbers often symbolize colder climates with larger heating calls for. Nevertheless, the precise traits of every zone can differ significantly relying on the area.
For instance, a Zone 4 would possibly symbolize a temperate local weather with average heating and cooling calls for, whereas a Zone 5 would possibly symbolize a hot-humid local weather with important cooling necessities. The delicate distinctions inside zones (e.g., 3A vs. 3B) usually mirror variations in humidity or photo voltaic radiation.
Purposes of the ASHRAE Local weather Zones Map:
The ASHRAE local weather zones map serves as an important device in quite a few features of constructing design and building:
- Vitality-efficient constructing design: The map is crucial for choosing applicable HVAC methods and constructing envelope designs. Buildings in hot-humid zones would require completely different methods than these in chilly climates. Understanding the native local weather permits architects and engineers to optimize constructing designs for minimal vitality consumption.
- Constructing codes and rules: Many constructing codes and vitality effectivity requirements make the most of the ASHRAE local weather zones to determine minimal necessities for constructing efficiency. This ensures that buildings are designed to fulfill the precise vitality calls for of their location.
- Materials choice: The local weather zone influences the number of constructing supplies. Supplies with excessive thermal resistance are essential in chilly climates to attenuate warmth loss, whereas supplies with excessive photo voltaic reflectance are vital in sizzling climates to cut back warmth achieve.
- HVAC system design: The selection of HVAC methods (heating, air flow, and air con) is immediately influenced by the local weather zone. Warmth pumps are more and more in style in average climates, whereas air con is crucial in sizzling and humid zones.
- Renewable vitality integration: The map helps decide the feasibility and effectivity of integrating renewable vitality applied sciences, akin to photo voltaic panels or geothermal warmth pumps, into constructing designs.
Limitations and Future Developments:
Whereas the ASHRAE local weather zones map is a worthwhile device, it has limitations:
- Spatial decision: The map’s decision may not seize the microclimatic variations inside a single zone. A big zone would possibly embody numerous microclimates, necessitating extra localized evaluation for exact design choices.
- Local weather change: The map relies on historic local weather knowledge. The impacts of local weather change, akin to rising temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns, will not be totally integrated into the present model. Future revisions might want to handle these evolving weather conditions.
- City warmth island impact: The map would not explicitly account for the city warmth island impact, the place city areas expertise increased temperatures than surrounding rural areas. This impact must be thought of individually throughout constructing design.
Future developments of the ASHRAE local weather zones map are more likely to give attention to:
- Increased decision knowledge: Incorporating extra granular local weather knowledge to enhance spatial accuracy and seize microclimatic variations.
- Local weather change projections: Integrating local weather change projections to anticipate future weather conditions and guarantee long-term constructing resilience.
- Dynamic modeling: Utilizing dynamic constructing simulation fashions to account for the advanced interactions between constructing design, local weather, and vitality consumption.
Conclusion:
The ASHRAE local weather zones map is a essential useful resource for sustainable constructing design. By understanding the climatic traits of a location, designers can create buildings which can be energy-efficient, comfy, and resilient to the impacts of local weather change. Whereas the map has limitations, its ongoing refinement and integration with superior modeling methods promise to reinforce its accuracy and relevance within the years to come back. The map stays an indispensable device for anybody striving to create environmentally accountable and high-performance buildings in a world going through more and more advanced climatic challenges. Its continued evolution ensures its continued significance in shaping the way forward for constructing design and building.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Decoding the ASHRAE Local weather Zones Map: A Complete Information to Local weather Classification. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!