Decoding the IECC Local weather Zone Map: A Complete Information to Constructing Codes and Vitality Effectivity
Associated Articles: Decoding the IECC Local weather Zone Map: A Complete Information to Constructing Codes and Vitality Effectivity
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the IECC Local weather Zone Map: A Complete Information to Constructing Codes and Vitality Effectivity. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the IECC Local weather Zone Map: A Complete Information to Constructing Codes and Vitality Effectivity
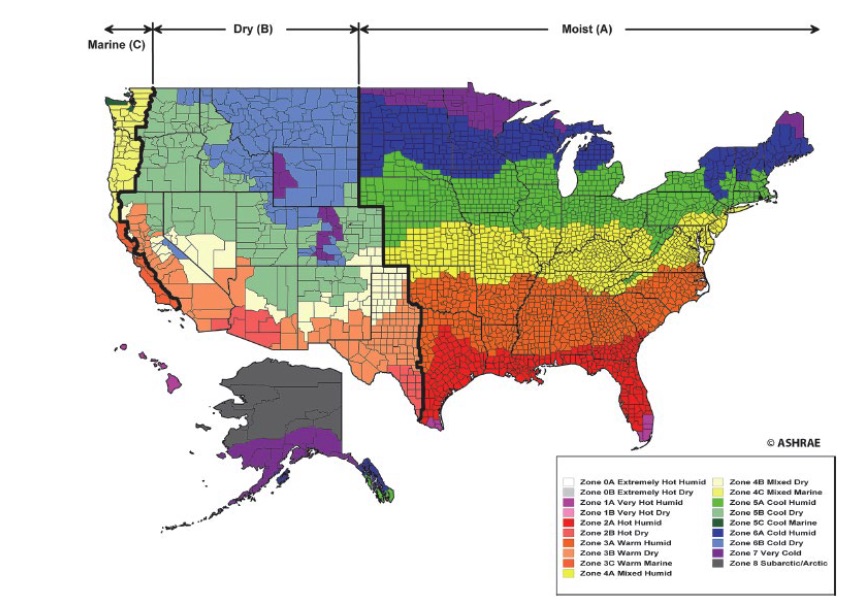
The Worldwide Vitality Conservation Code (IECC), a broadly adopted customary for energy-efficient constructing design, makes use of a local weather zone map to categorize areas based mostly on their climate traits. This map is essential for figuring out the minimal power effectivity necessities for brand spanking new buildings inside every zone. Understanding the IECC local weather zone map is paramount for architects, builders, engineers, and policymakers striving to create sustainable and energy-conscious buildings. This text delves into the intricacies of this map, exploring its methodology, implications for constructing design, and ongoing evolution in response to local weather change.
The Basis of the IECC Local weather Zone Map:
The IECC local weather zone map just isn’t a static entity. It is periodically up to date to mirror developments in local weather modeling, information assortment, and power effectivity applied sciences. The map’s basis lies within the evaluation of long-term climate information, particularly specializing in parameters essential for constructing power efficiency:
-
Heating Diploma Days (HDD): A measure of the cumulative temperature distinction between the common each day temperature and a base temperature (sometimes 65°F or 18°C). Increased HDD values point out a colder local weather requiring extra heating power.
-
Cooling Diploma Days (CDD): A measure of the cumulative temperature distinction between the common each day temperature and a base temperature (sometimes 65°F or 18°C). Increased CDD values point out a hotter local weather demanding extra cooling power.
-
Humidity: Excessive humidity ranges influence each heating and cooling hundreds, influencing the design of HVAC programs and constructing envelope elements.
-
Photo voltaic Radiation: The quantity of photo voltaic power obtained influences passive photo voltaic design methods and the sizing of photo voltaic power programs.
-
Wind Velocity and Path: These elements have an effect on constructing envelope design, pure air flow methods, and the efficiency of renewable power programs.
Utilizing subtle algorithms and local weather fashions, these information factors are processed to outline distinct local weather zones, every with its distinctive power efficiency traits. This ensures that power codes mirror the precise weather conditions of every area, selling power effectivity with out imposing unnecessarily stringent necessities in milder climates or overly lenient ones in excessive climates.
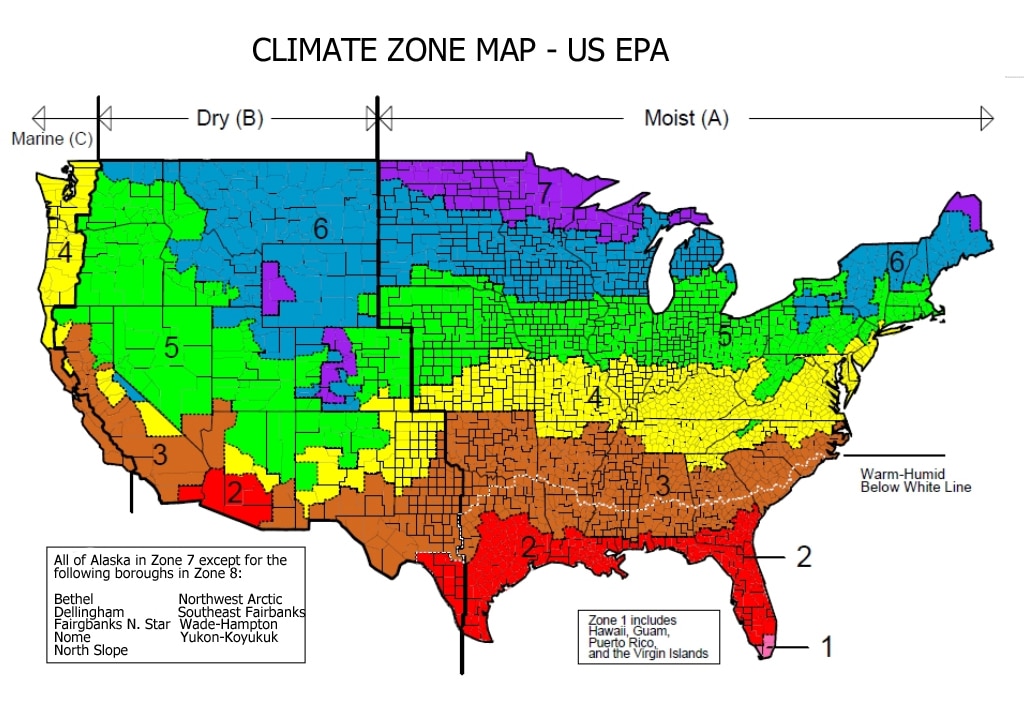
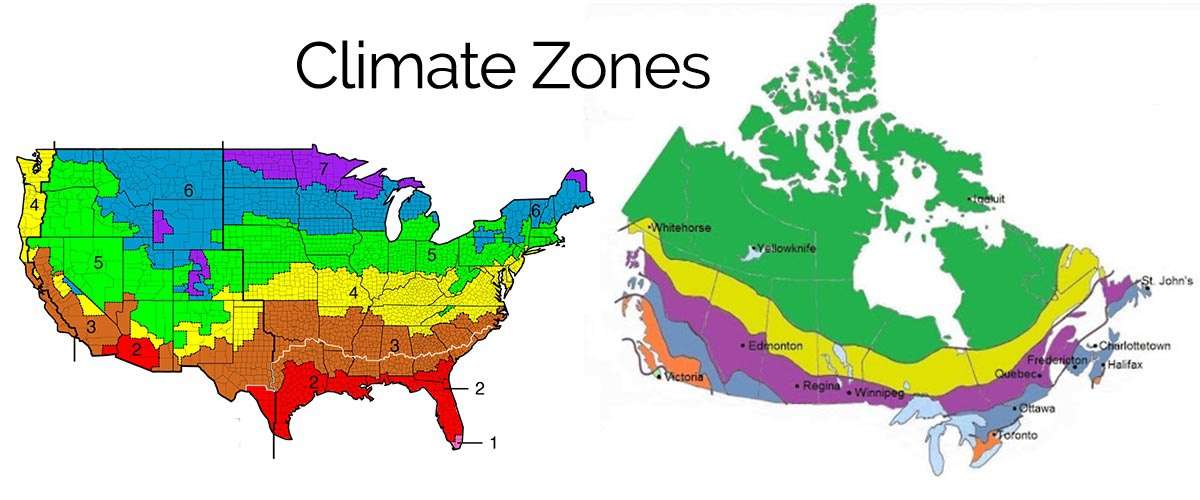
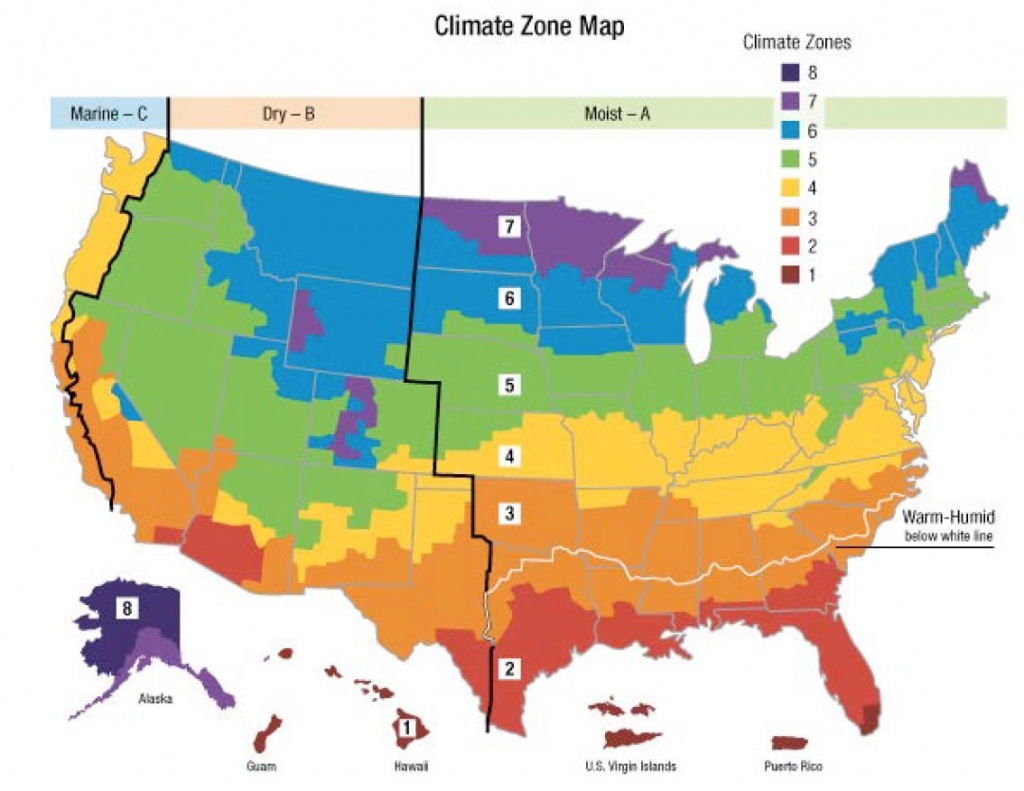
Understanding the Zones:
The IECC local weather zone map sometimes divides areas into a number of local weather zones, though the precise quantity and designations may fluctuate barely relying on the precise version of the code. Typically, the zones are categorized from 1A (coldest) to eight (hottest and humidest), with additional subdivisions inside these broad classes to account for nuances in local weather. For instance, a zone could be additional categorized as a "1A" or "1B" sub-zone, reflecting barely totally different HDDs and different climatic elements. This granularity permits for a extra exact tailoring of power codes to particular native situations.
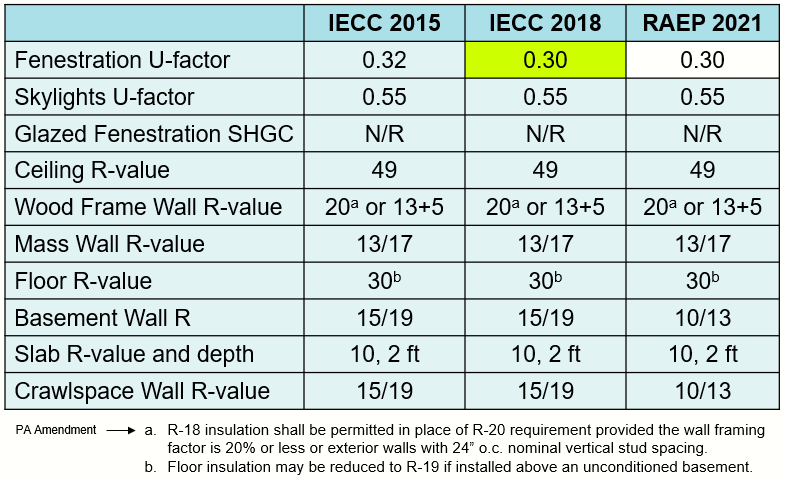
Implications for Constructing Design and Development:
The assigned local weather zone straight impacts a number of points of constructing design and development, together with:
-
Constructing Envelope: Colder zones necessitate greater ranges of insulation, tighter air sealing, and extra environment friendly home windows to attenuate warmth loss. Hotter zones prioritize shading, thermal mass, and high-performance glazing to cut back cooling hundreds.
-
HVAC Programs: The scale and sort of heating and cooling programs are decided by the zone’s heating and cooling calls for. Colder zones typically require bigger furnaces and warmth pumps, whereas hotter zones necessitate extra highly effective air con models.
-
Home equipment and Tools: Vitality effectivity requirements for home equipment and tools are sometimes tied to the local weather zone, requiring greater effectivity ranges in zones with higher power calls for.
-
Renewable Vitality Programs: The local weather zone influences the feasibility and effectiveness of renewable power applied sciences. Photo voltaic power programs are extra productive in sunnier zones, whereas wind power programs are extra appropriate in windier areas.
-
Water Heating: Local weather zones influence the design and effectivity of water heating programs, with colder zones requiring extra environment friendly programs to satisfy greater scorching water calls for.
Evolution of the IECC Local weather Zone Map and Future Concerns:
The IECC local weather zone map just isn’t a static doc. As local weather change alters climate patterns and intensifies excessive climate occasions, the map requires periodic updates to precisely mirror these shifts. The rising frequency and depth of warmth waves, for instance, are resulting in greater CDD values in lots of areas, necessitating changes to cooling necessities within the corresponding local weather zones. Equally, modifications in precipitation patterns and elevated occurrences of maximum chilly snaps can affect HDD values and necessitate modifications to heating necessities.
Future iterations of the IECC local weather zone map will doubtless incorporate extra subtle local weather modeling methods, incorporating higher-resolution information and extra superior predictive fashions to account for the continuing impacts of local weather change. This may contain:
-
Incorporating local weather projections: Future maps will doubtless combine local weather change projections to anticipate future shifts in local weather patterns and be certain that constructing codes stay related and efficient in the long run.
-
Elevated information granularity: The usage of higher-resolution local weather information will permit for a extra exact delineation of local weather zones, resulting in extra tailor-made power effectivity necessities.
-
Dynamic zone changes: Future maps may incorporate mechanisms for dynamic zone changes, permitting for extra responsive updates as local weather patterns evolve.
Past the Map: A Holistic Method to Vitality Effectivity:
Whereas the IECC local weather zone map is a vital instrument for establishing minimal power effectivity requirements, it is important to keep in mind that it is just one element of a broader technique for sustainable constructing design. Different elements, corresponding to constructing orientation, web site choice, and using passive design methods, considerably influence power efficiency. A holistic strategy that integrates the local weather zone map with different sustainable design ideas is critical to create actually energy-efficient and environmentally accountable buildings.
Conclusion:
The IECC local weather zone map is a basic instrument for selling power effectivity in constructing design. Its evolution displays developments in local weather modeling and power effectivity know-how, making certain that constructing codes stay related and efficient within the face of a altering local weather. By understanding the implications of the local weather zone map and integrating it right into a holistic strategy to sustainable constructing design, we are able to create buildings which are each energy-efficient and environmentally accountable, contributing to a extra sustainable future. Ongoing analysis and updates to the map are essential to make sure its continued effectiveness in navigating the challenges of local weather change and selling resilient, energy-conscious buildings for generations to return.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Decoding the IECC Local weather Zone Map: A Complete Information to Constructing Codes and Vitality Effectivity. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!