Decoding the Sierra Madre Oriental: A Geographic and Ecological Exploration
Associated Articles: Decoding the Sierra Madre Oriental: A Geographic and Ecological Exploration
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Sierra Madre Oriental: A Geographic and Ecological Exploration. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Sierra Madre Oriental: A Geographic and Ecological Exploration
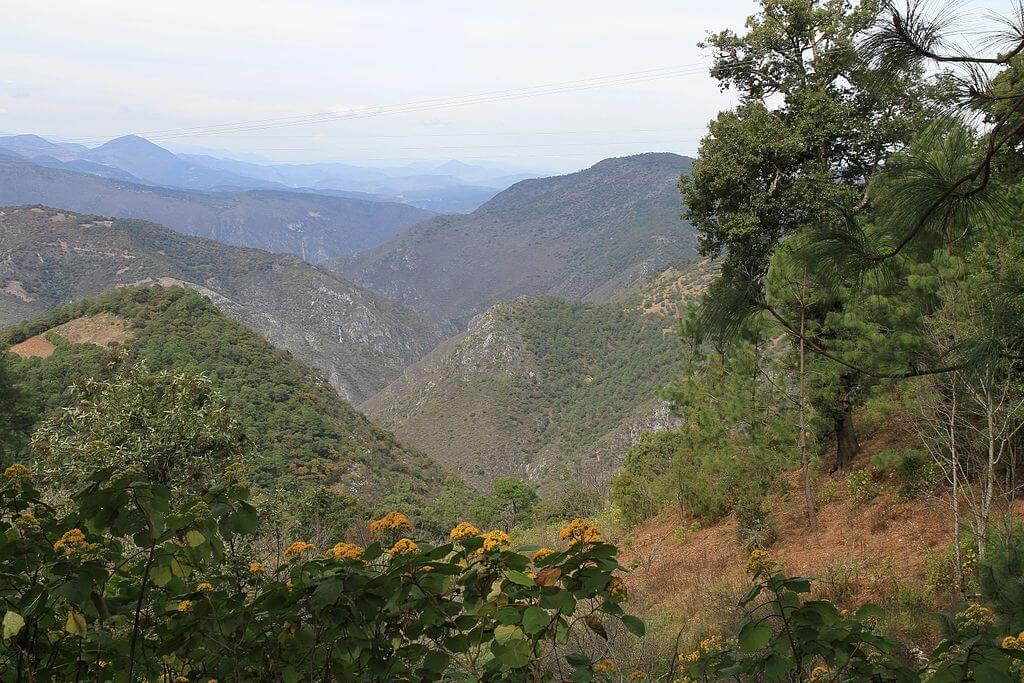

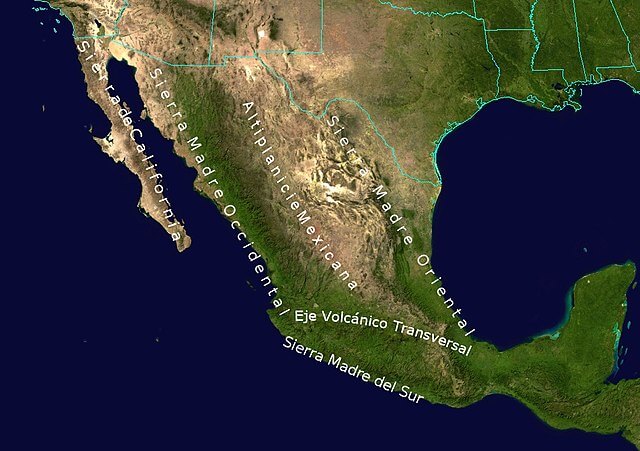
The Sierra Madre Oriental, a formidable mountain vary stretching throughout northeastern Mexico, is a area of immense geographical and ecological significance. Its rugged peaks, deep canyons, and various ecosystems harbor a wealth of biodiversity and maintain an important place within the nation’s historical past and tradition. This text delves into the complexities of the Sierra Madre Oriental, exploring its geological formation, ecological range, human impression, and the challenges going through its future conservation. Whereas a static map can not absolutely seize the dynamic nature of this area, understanding its cartographic illustration is essential to appreciating its intricacies.
Geological Genesis: A Story Etched in Stone
The Sierra Madre Oriental’s story begins hundreds of thousands of years in the past, formed by tectonic forces that proceed to affect its panorama at present. The vary is primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, largely limestone and shale, deposited over huge intervals in historic seas. The Laramide Orogeny, a interval of intense mountain constructing that occurred throughout the Late Cretaceous and Early Paleogene epochs (roughly 70-40 million years in the past), performed an important position in its formation. This tectonic occasion resulted within the uplift and folding of those sedimentary layers, creating the attribute north-south orientation of the vary.
A map of the Sierra Madre Oriental would spotlight its distinct physiographic provinces. The vary is not a uniform entity; it contains a collection of parallel ridges and valleys, exhibiting various altitudes and geological options. The western slopes, usually steeper and extra rugged, typically descend abruptly into the arid lands of the Mexican Plateau. The japanese slopes, whereas nonetheless steep in locations, transition extra regularly into the coastal plains and the Gulf of Mexico. These variations are mirrored within the various drainage patterns, with quite a few rivers carving their method via the mountains, feeding into main river methods just like the Rio Grande and the Pánuco. An in depth map would present the intricate community of those rivers and streams, essential for understanding water assets and biodiversity distribution.
Ecological Tapestry: Biodiversity Hotspot
The Sierra Madre Oriental’s dramatic topography helps a panoramic array of ecosystems, starting from arid scrublands at decrease elevations to cloud forests and pine-oak forests at larger altitudes. This vertical zonation, clearly seen on a well-detailed map, is a key think about its distinctive biodiversity. The vary is acknowledged as a world biodiversity hotspot, harboring a big variety of endemic species – crops and animals discovered nowhere else on Earth.
At decrease elevations, the arid and semi-arid ecosystems help drought-tolerant wildlife. As altitude will increase, the local weather turns into cooler and wetter, resulting in the event of lusher vegetation. Pine-oak forests dominate mid-elevations, offering habitat for a wealthy range of mammals, birds, and reptiles. Increased up, cloud forests, perpetually shrouded in mist, create a singular setting for specialised species tailored to excessive humidity and comparatively cool temperatures. These cloud forests are significantly susceptible to habitat loss and local weather change, making their conservation a vital precedence. A map displaying vegetation zones would vividly illustrate this transition and spotlight areas of excessive conservation worth.
The map would additionally want to point the presence of protected areas, akin to nationwide parks and reserves, that are essential for safeguarding the area’s biodiversity. These areas typically embody a consultant vary of ecosystems, offering refuge for endangered species and selling ecological analysis. Understanding the distribution of those protected areas is essential for efficient conservation methods.
Human Influence and Challenges:
The Sierra Madre Oriental has an extended historical past of human interplay. Indigenous communities have inhabited the area for millennia, growing sustainable practices tailored to its various environments. Nevertheless, more moderen human actions have positioned vital stress on the area’s ecological integrity.
Deforestation, pushed by agricultural growth, logging, and mining, is a significant concern. A comparability of historic and modern maps would starkly reveal the extent of forest loss over time. This deforestation not solely reduces biodiversity but in addition contributes to soil erosion, elevated sedimentation in rivers, and modifications in native local weather patterns. Moreover, unsustainable agricultural practices can result in land degradation and desertification.
The extraction of pure assets, akin to minerals and timber, additionally poses vital challenges. Mining actions can result in habitat destruction, water air pollution, and social conflicts. Equally, unsustainable logging practices deplete forest assets and disrupt ecosystem features. A map highlighting areas of mining and logging exercise would supply invaluable insights into the spatial distribution of those impacts.
Conservation and Sustainable Growth:
Defending the Sierra Madre Oriental requires a multi-faceted method that integrates conservation efforts with sustainable growth methods. This consists of strengthening protected areas, selling sustainable forestry practices, supporting sustainable agriculture, and fostering community-based conservation initiatives. A map may successfully showcase areas focused for reforestation, community-managed forests, or ecotourism initiatives.
Moreover, selling ecotourism can present financial alternatives for native communities whereas concurrently elevating consciousness concerning the area’s ecological significance. Cautious planning and administration are important to make sure that tourism actions don’t negatively impression the setting.
Efficient conservation requires collaboration amongst authorities businesses, non-governmental organizations, native communities, and researchers. Sharing info and coordinating efforts via a well-maintained GIS (Geographic Info System) database, linked to an in depth and commonly up to date map, is essential for profitable conservation outcomes.
Conclusion:
The Sierra Madre Oriental is a treasure trove of biodiversity and geological wonders. Its distinctive ecosystems and wealthy cultural heritage are invaluable property to Mexico and the world. Nevertheless, the vary faces vital challenges as a result of human actions. By integrating scientific understanding, conservation methods, and sustainable growth practices, knowledgeable by detailed and commonly up to date maps, we are able to work in direction of making certain the long-term well being and integrity of this outstanding mountain vary for generations to come back. The map, due to this fact, shouldn’t be merely a static illustration; it’s a dynamic device for understanding, managing, and in the end, preserving this important ecosystem.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Decoding the Sierra Madre Oriental: A Geographic and Ecological Exploration. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!