Finding Iraq: A Geographic and Geopolitical Examination
Associated Articles: Finding Iraq: A Geographic and Geopolitical Examination
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Finding Iraq: A Geographic and Geopolitical Examination. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Finding Iraq: A Geographic and Geopolitical Examination
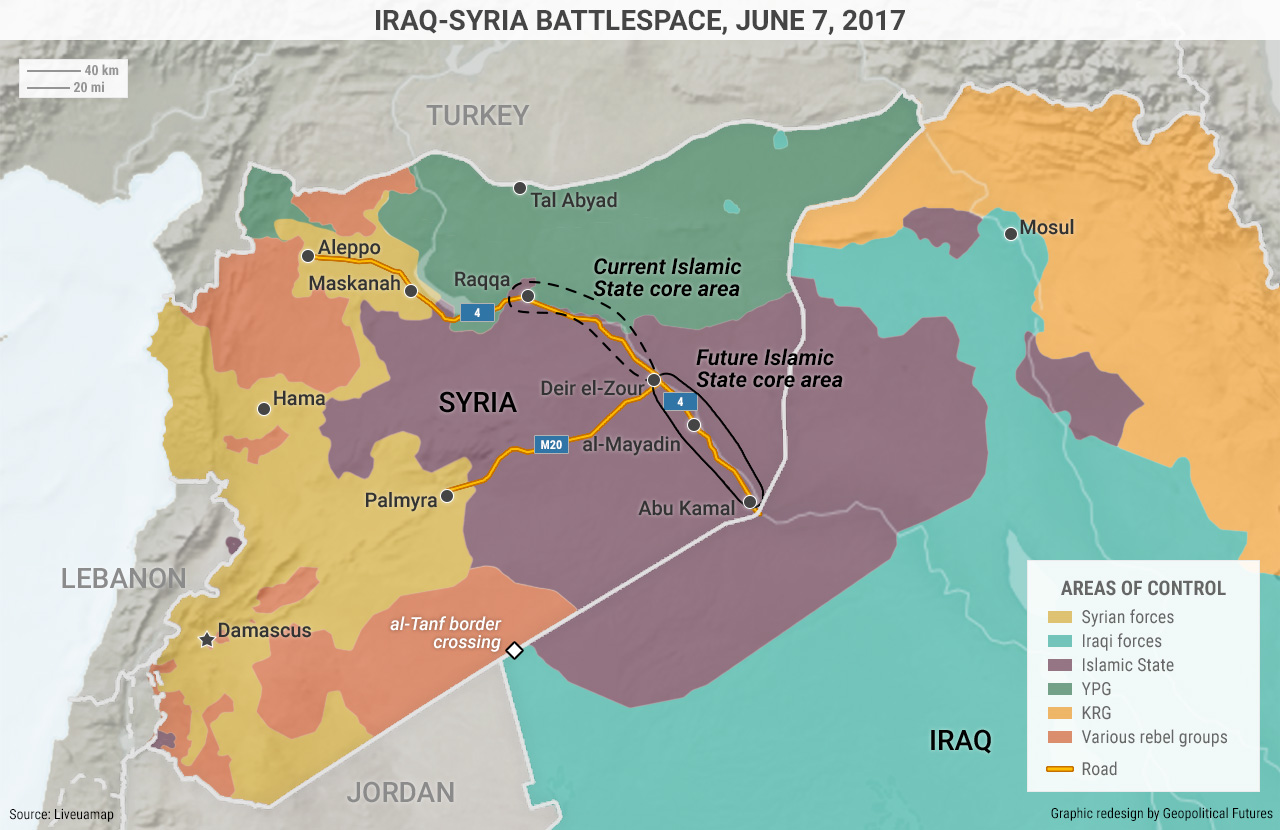
Iraq, formally the Republic of Iraq, holds a pivotal place within the Center East, a area steeped in historical past and at the moment grappling with advanced geopolitical dynamics. Pinpointing its location on a map reveals not solely its geographical coordinates but additionally its strategic significance and the components shaping its previous, current, and future. This text will delve into the exact location of Iraq, exploring its bordering nations, its inside geography, and the geopolitical implications of its location.
Geographical Coordinates and Regional Context:
Iraq is located in Western Asia, particularly within the northeastern nook of the Arabian Peninsula. Its exact location might be summarized as mendacity between latitudes 29° and 38° North and longitudes 39° and 49° East. This locations it in a area characterised by arid and semi-arid climates, with vital variations in elevation and terrain throughout its borders.
To visualise Iraq’s location, think about a map of the Center East. It is nestled between a number of key nations, every contributing to its advanced geopolitical panorama:
-
To the north: Iraq shares a border with Turkey and a small part with Syria. The mountainous northern areas bordering Turkey and Syria are considerably totally different from the flat, desert areas to the south. This northern border area has traditionally been a web site of battle and migration.
-
To the east: Iran kinds a good portion of Iraq’s jap border. This shared border, stretching for a whole bunch of kilometers, is an important consider Iraq’s relationship with Iran, a serious regional energy. The proximity fuels each cooperation and competitors, relying on the prevailing political local weather.
-
To the south: Iraq borders Kuwait and the Persian Gulf. This southern shoreline, although comparatively quick in comparison with its different borders, offers entry to important maritime commerce routes and vital oil reserves. The connection with Kuwait has been traditionally fraught, significantly following the Iraqi invasion of 1990.
-
To the west: Iraq shares a border with Jordan and Saudi Arabia. These western borders are much less densely populated than the jap and northern ones, however they continue to be strategically essential, significantly within the context of regional safety considerations.
Inner Geography and its Affect:
Iraq’s inside geography is as various as its bordering nations. It is not a uniformly flat desert; moderately, it encompasses a wide range of landscapes:
-
Mesopotamia: The heartland of Iraq, Mesopotamia (which means "between the rivers"), lies between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. This fertile crescent, traditionally often called the cradle of civilization, has supported agriculture and dense populations for millennia. Its wealthy alluvial soil, as soon as the supply of prosperity, is now going through challenges from water shortage and desertification.
-
The Zagros Mountains: Within the northeast, the Zagros Mountains type a pure barrier, creating a definite local weather and influencing the distribution of inhabitants. These mountains are house to Kurdish communities, whose quest for autonomy has formed Iraq’s political historical past.
-
The Arabian Desert: A lot of Iraq’s western and southern areas encompass huge stretches of desert. This harsh setting poses challenges to agriculture and infrastructure improvement but additionally holds vital oil reserves, a key driver of Iraq’s financial system.
-
The Mesopotamian Marshes: Positioned in southern Iraq, these in depth marshlands have been as soon as a thriving ecosystem, house to various natural world and varied communities. Nevertheless, they have been severely broken by Saddam Hussein’s regime, leading to environmental and social penalties that proceed to be addressed.
Geopolitical Significance of Iraq’s Location:
Iraq’s location on the crossroads of a number of main areas and civilizations has made it a focus of geopolitical competitors and battle for hundreds of years. Its strategic significance stems from a number of components:
-
Oil Reserves: Iraq possesses substantial oil reserves, putting it among the many world’s main oil producers. This makes it an important participant in world vitality markets and a goal for each financial and political affect.
-
Regional Energy Dynamics: Its proximity to Iran, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia, all regional powers with competing pursuits, makes Iraq a key participant in regional energy dynamics. The steadiness of energy within the area considerably impacts Iraq’s stability and safety.
-
Commerce Routes: Iraq’s location alongside historic commerce routes connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe has contributed to its cultural range and its significance in regional commerce. The event of contemporary infrastructure, together with ports and pipelines, additional enhances its strategic significance.
-
Spiritual and Cultural Significance: Iraq is a land of serious spiritual and cultural significance, house to websites sacred to Islam, Christianity, and different faiths. This heritage contributes to its world significance but additionally presents challenges in navigating various spiritual and ethnic identities.
Conclusion:
Pinpointing Iraq on a map requires understanding not solely its geographical coordinates but additionally the advanced interaction of its inside geography and its regional context. Its location on the coronary heart of the Center East, with its various landscapes, wealthy historical past, and substantial oil reserves, has made it a strategically important and sometimes risky area. Understanding Iraq’s location is essential for greedy the geopolitical forces shaping the Center East and the challenges and alternatives going through this traditionally vital nation. Its future trajectory will rely on the way it navigates the advanced dynamics of its inside divisions and its relationships with its highly effective neighbors. The map of Iraq, due to this fact, isn’t just a static illustration of geographical boundaries, however a dynamic illustration of a nation grappling with its previous and striving for a secure future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Finding Iraq: A Geographic and Geopolitical Examination. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!