Navigating the Metropolis on Two Wheels: A Deep Dive into the Divvy Bike Map and its Implications
Associated Articles: Navigating the Metropolis on Two Wheels: A Deep Dive into the Divvy Bike Map and its Implications
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the Metropolis on Two Wheels: A Deep Dive into the Divvy Bike Map and its Implications. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Metropolis on Two Wheels: A Deep Dive into the Divvy Bike Map and its Implications

Chicago’s Divvy bike-sharing system is greater than only a handy mode of transportation; it is a dynamic, evolving community that displays town’s infrastructure, its demographics, and the evolving panorama of city mobility. Understanding this technique requires extra than simply hopping on a motorcycle; it calls for a cautious examination of its underlying map, its information, and the implications of its design. This text delves into the intricacies of the Divvy bike map, exploring its performance, its limitations, and its broader significance throughout the context of city planning and sustainable transportation.
The Divvy Bike Map: A Person’s Perspective
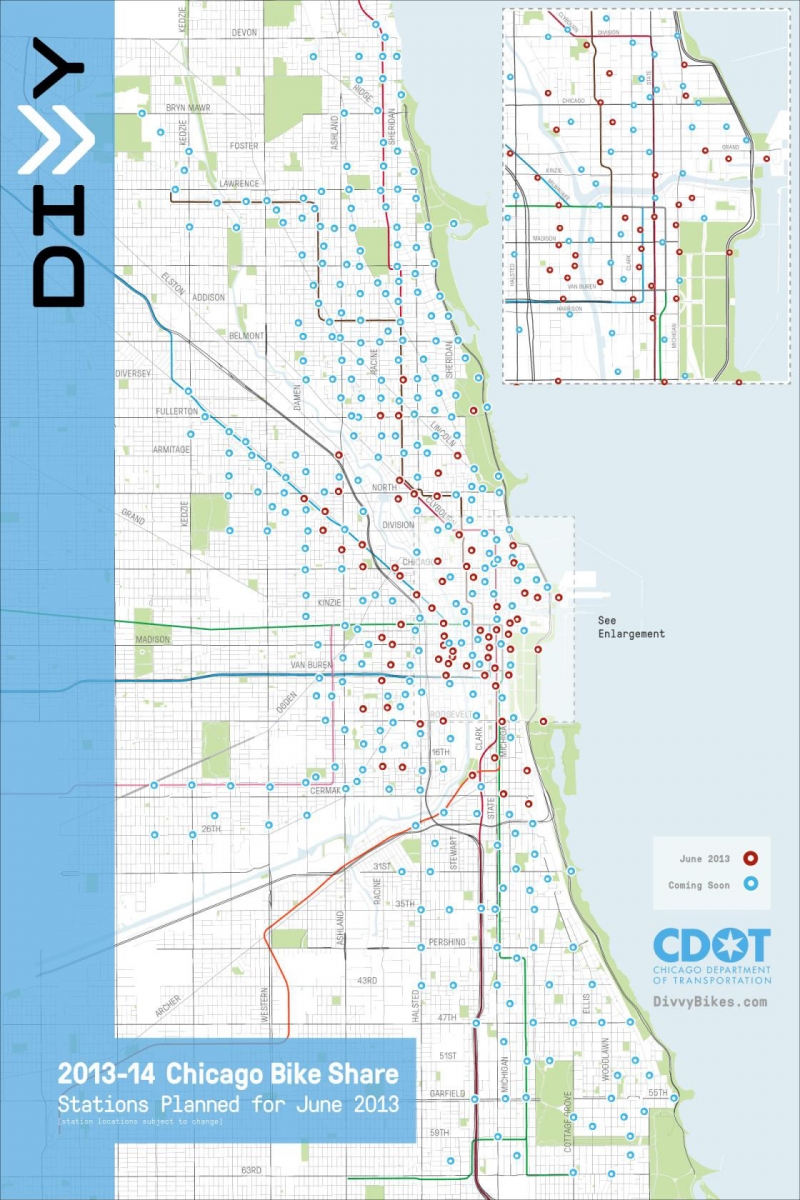
The Divvy bike map, accessible via the Divvy app and web site, serves because the central hub for customers to work together with the system. At its core, it is a visually wealthy illustration of the bike stations scattered throughout Chicago and its surrounding suburbs. Every station is represented by a definite icon, often a bicycle image, indicating its location, the variety of obtainable bikes and docks, and probably real-time information on the station’s standing (e.g., full, empty, or partially full).
The map’s performance extends past easy location identification. Customers can:
- Find close by stations: The map makes use of GPS to pinpoint the consumer’s location and show the closest stations, sorted by distance. This characteristic is essential for each discovering a motorcycle and returning it conveniently.
- Test bike and dock availability: Actual-time information updates present essential details about the variety of obtainable bikes and empty docks at every station. This prevents customers from biking to a station solely to seek out it full or empty.
- Plan routes: Whereas not a classy route planner like Google Maps, the map typically offers primary route solutions based mostly on proximity and station connectivity. That is useful for shorter journeys however is probably not optimum for longer commutes or complicated journeys.
- Filter stations: Customers can typically filter stations based mostly on particular standards, corresponding to availability of electrical bikes or the presence of accessible docks.
- Entry station info: Clicking on a station icon often offers extra particulars, corresponding to its tackle, working hours, and potential accessibility options.
Past the Floor: Knowledge and Algorithmics
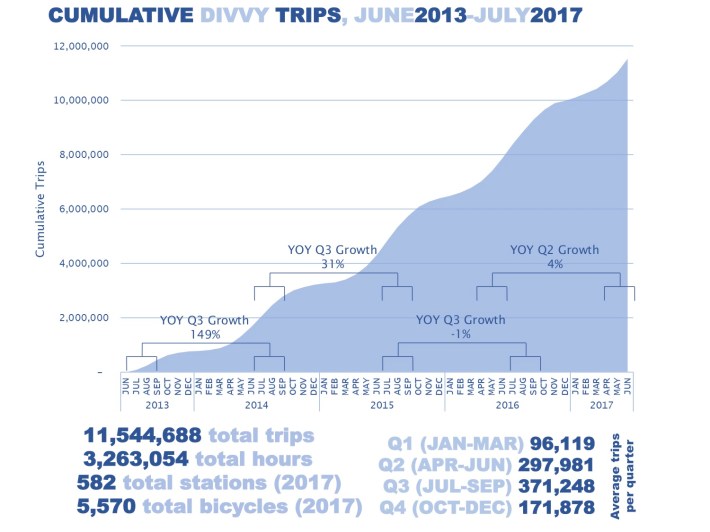
The seemingly easy map is underpinned by a fancy system of information assortment, processing, and visualization. The actual-time updates on bike and dock availability depend on sensors embedded inside every station, consistently transmitting info to central servers. This information is then processed and displayed on the map, offering customers with an up-to-the-minute view of the system’s standing.
The algorithms behind the map’s performance are equally necessary. These algorithms decide how stations are displayed, how routes are steered, and the way the system manages potential imbalances in bike distribution. For example, if one space persistently has extra bikes than docks, the algorithms may set off a rebalancing operation, involving Divvy workers and even automated programs, to redistribute bikes to areas with greater demand.
The accuracy and reliability of this information are essential for the system’s effectiveness. Inaccurate info can result in frustration for customers, wasted time, and probably missed alternatives. The system’s builders consistently work on bettering information accuracy and algorithm effectivity to make sure a easy consumer expertise.
The Map as a Reflection of City Infrastructure and Fairness
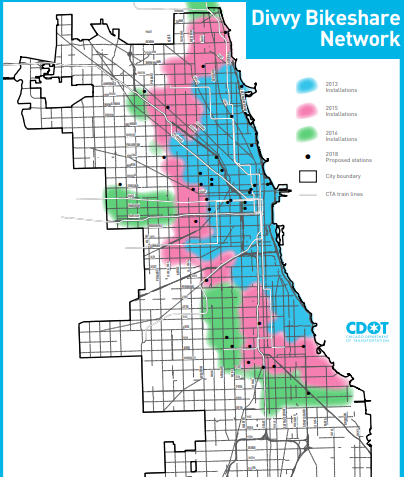
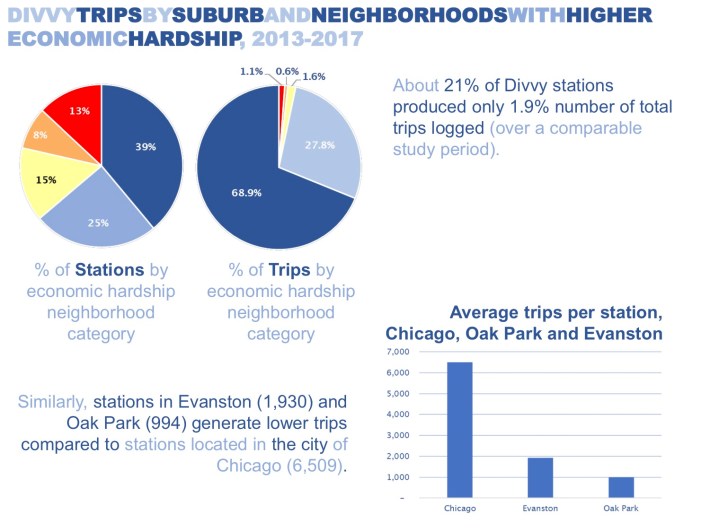
The Divvy bike map just isn’t merely a technological instrument; it is a visible illustration of Chicago’s city infrastructure and its inherent inequalities. The density and distribution of motorcycle stations mirror town’s planning priorities and funding patterns. Areas with excessive station density typically correlate with greater inhabitants density, business exercise, and entry to public transportation.
Nevertheless, the map additionally highlights disparities in entry to bike-sharing companies. Areas with decrease station density, typically in underserved communities, expertise restricted entry to this handy and sustainable mode of transportation. This disparity raises necessary questions on fairness and the necessity for equitable distribution of bike-sharing infrastructure. Addressing this requires cautious consideration of things corresponding to inhabitants density, socioeconomic standing, and accessibility for folks with disabilities.
Limitations and Challenges
Regardless of its performance, the Divvy bike map has limitations:
- Restricted route planning capabilities: The map’s route planning options are primary and will not account for components corresponding to elevation, site visitors, or pedestrian crossings, making it much less appropriate for longer or complicated journeys.
- Knowledge inaccuracies: Whereas efforts are made to make sure information accuracy, real-time updates can typically be delayed or inaccurate, resulting in consumer frustration. Elements like sensor malfunctions or community points can contribute to those inaccuracies.
- Lack of integration with different transportation modes: The map typically lacks seamless integration with different transportation modes, corresponding to public transit, making journey planning involving a number of modes much less handy.
- Accessibility issues: Whereas efforts are made to offer accessible stations, the map might not at all times clearly point out the extent of accessibility at every station, posing challenges for customers with disabilities.
- Dynamic Demand: The map struggles to foretell and adapt to sudden shifts in demand, corresponding to giant occasions or surprising climate adjustments. This may result in momentary shortages or surpluses of bikes in sure areas.
Future Instructions and Improvements
The Divvy bike map is consistently evolving. Future enhancements might embrace:
- Enhanced route planning: Integrating extra refined algorithms that take into account components like site visitors, elevation, and pedestrian crossings might considerably enhance route planning capabilities.
- Improved information accuracy: Investing in additional strong sensor know-how and community infrastructure might decrease information inaccuracies and guarantee real-time updates.
- Integration with different transportation modes: Seamless integration with public transit apps and different transportation companies might create a extra complete and user-friendly journey planning expertise.
- Enhanced accessibility info: Offering extra detailed and correct details about station accessibility for customers with disabilities is essential for selling inclusivity.
- Predictive analytics: Utilizing machine studying to foretell demand fluctuations and proactively rebalance the system might enhance effectivity and consumer satisfaction.
- Integration with different micro-mobility companies: Integrating details about different micro-mobility companies, corresponding to scooters and e-bikes, might present customers with a wider vary of transportation choices.
Conclusion: The Divvy Bike Map as a Instrument for City Transformation
The Divvy bike map is greater than only a navigational instrument; it is a window into the complexities of city planning, sustainable transportation, and social fairness. Its design, information, and limitations mirror the challenges and alternatives of making a really accessible and environment friendly bike-sharing system. By addressing the challenges and embracing innovation, the Divvy bike map can play a good larger function in shaping Chicago’s future as a extra sustainable and equitable metropolis. The continuing evolution of the map, pushed by technological developments and a dedication to consumer expertise and equitable entry, will probably be essential in figuring out its long-term success and its contribution to the broader targets of city mobility and sustainable transportation. The map, due to this fact, just isn’t merely a static illustration of the Divvy system however a dynamic instrument for city transformation, consistently adapting and evolving alongside town it serves.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Navigating the Metropolis on Two Wheels: A Deep Dive into the Divvy Bike Map and its Implications. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!