Navigating the Italian Peninsula: A Deep Dive into Italy’s Geography and its Place inside Europe
Associated Articles: Navigating the Italian Peninsula: A Deep Dive into Italy’s Geography and its Place inside Europe
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Navigating the Italian Peninsula: A Deep Dive into Italy’s Geography and its Place inside Europe. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Italian Peninsula: A Deep Dive into Italy’s Geography and its Place inside Europe

Italy, a boot-shaped peninsula jutting into the Mediterranean Sea, holds a singular and pivotal place on the European map. Its geography, a posh interaction of mountains, plains, and coastlines, has profoundly formed its historical past, tradition, and even its fashionable political panorama. Understanding Italy’s location and its inner geographical options is essential to appreciating its wealthy tapestry of regional identities and its enduring affect on European affairs.
Italy’s Place in Europe: A Crossroads of Civilizations
A look at a map of Europe instantly highlights Italy’s strategic location. Located in Southern Europe, it acts as a bridge between Western and Japanese Europe, connecting the Iberian Peninsula to the Balkans. Its proximity to North Africa and the Center East has additionally positioned it on the coronary heart of historic commerce routes and cultural exchanges for millennia. This central place has made Italy a crossroads of civilizations, leading to an enchanting mix of influences all through its historical past. The Roman Empire, originating in Italy, expanded its affect throughout the Mediterranean, leaving an indelible mark on European tradition and governance. Later, the Italian Renaissance, a interval of inventive and mental flourishing, unfold its affect throughout Europe, shaping inventive kinds and philosophical thought.
The nation’s geographical options additional reinforce its significance. The Alps, a formidable mountain vary within the north, have traditionally supplied a pure barrier, but additionally served as a conduit for commerce and migration. The Apennine Mountains, working the size of the Italian peninsula, divide the nation, creating distinct regional identities and influencing the event of impartial city-states throughout the medieval interval. These mountains additionally affect local weather and agricultural practices, resulting in various regional cuisines and economies. The Po Valley, a fertile plain in Northern Italy, is an important agricultural area, whereas the coastal plains alongside the Mediterranean and Adriatic seas have fostered thriving port cities and maritime traditions.
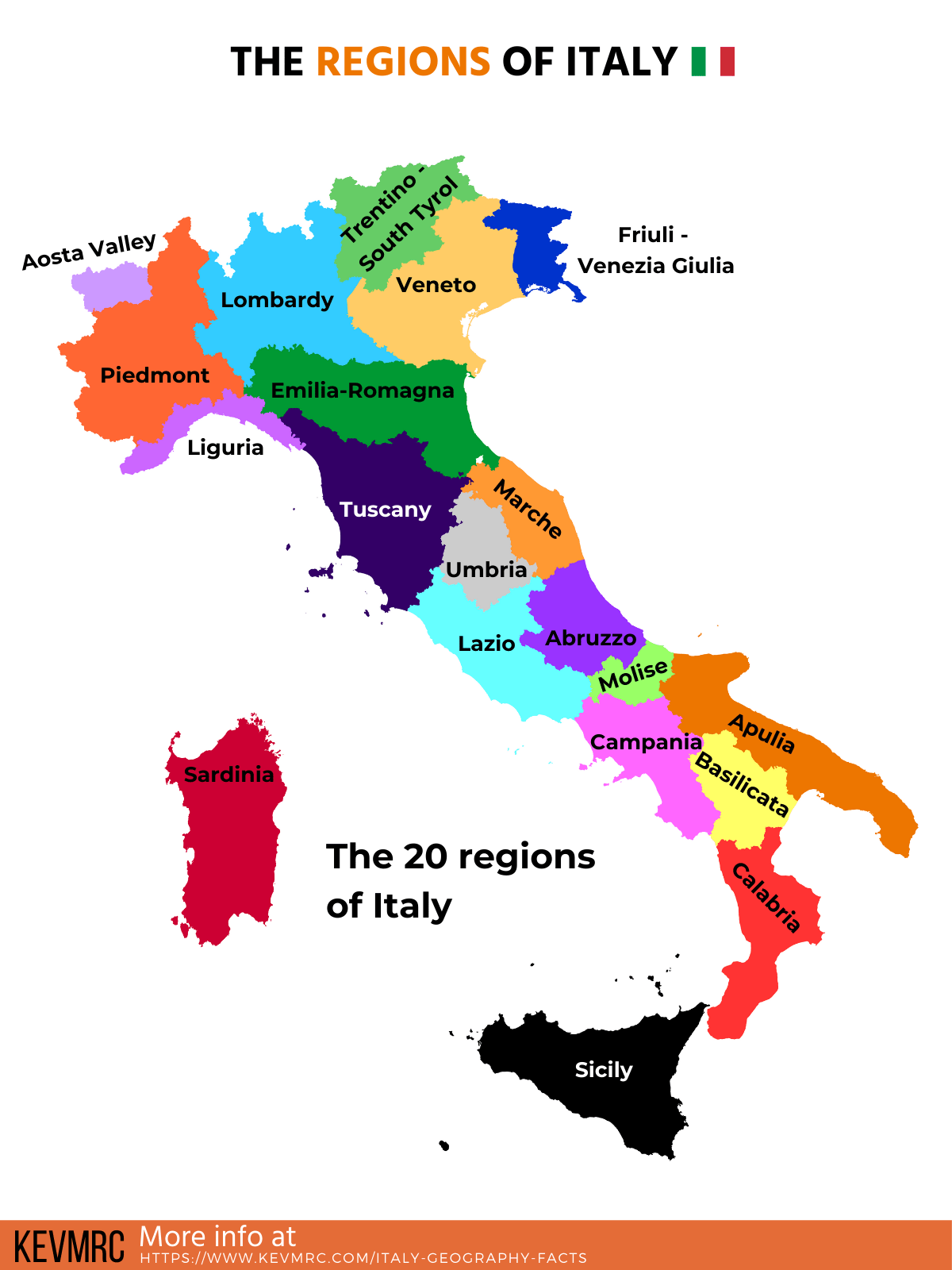
The Italian Peninsula: A Nearer Have a look at Regional Geography
Analyzing an in depth map of Italy reveals a posh interaction of geographical options which have formed its various areas. The nation might be broadly divided into 5 main geographical areas:
-
The North: Dominated by the Alps and the Po Valley, this area is characterised by its fertile plains, appropriate for agriculture, and its industrial facilities. The Alps present hydroelectric energy and alternatives for tourism, whereas the Po Valley produces vital agricultural output, together with rice, wheat, and corn. Main cities like Milan, Turin, and Venice are located on this area, every reflecting the distinctive influences of its location. The Alps additionally create distinct microclimates, resulting in variations in agriculture and life.
-
The Apennine Mountains: This central backbone of the Italian peninsula runs from north to south, dividing the nation into jap and western slopes. The mountains are characterised by rugged terrain, restricted arable land, and smaller, remoted communities. The Apennines have traditionally hindered communication and transportation, contributing to the event of distinct regional cultures and dialects. Nevertheless, the mountains additionally provide scenic magnificence and alternatives for tourism, notably in areas just like the Abruzzo Nationwide Park.
-
The Western Coast: This area encompasses the Ligurian coast, identified for its picturesque Cinque Terre villages, and the Tuscan coast, famed for its rolling hills, vineyards, and olive groves. The area is characterised by a Mediterranean local weather, with heat, dry summers and gentle, moist winters, supreme for cultivating grapes and olives. Coastal cities like Genoa and Livorno have performed vital roles in Italian maritime historical past and commerce.
-
The Central Area: This space encompasses Tuscany, Umbria, Lazio, and Marche, a mix of rolling hills, fertile valleys, and mountain ranges. The area is famend for its artwork, historical past, and delicacies. Rome, the capital metropolis, situated in Lazio, holds immense historic and cultural significance, whereas Florence, in Tuscany, is a middle for artwork and Renaissance historical past. The area’s geographical variety contributes to quite a lot of agricultural merchandise and a wealthy cultural heritage.
-
The South and Islands: This area consists of the areas of Campania, Puglia, Calabria, Basilicata, Sicily, and Sardinia. The southern a part of the Italian peninsula is characterised by a drier local weather and extra rugged terrain than the north. The islands of Sicily and Sardinia provide distinctive landscapes, from volcanic mountains to sandy seashores. This area is wealthy in historical past, with historical Greek and Roman ruins scattered all through the panorama. Agriculture performs a significant position within the southern financial system, with the cultivation of citrus fruits, olives, and grapes being notably essential.
The Impression of Geography on Italian Tradition and Society
Italy’s various geography has profoundly formed its tradition and society. The mountainous terrain contributed to the event of impartial city-states throughout the Center Ages, every with its personal distinct character and political system. The coastal areas fostered maritime traditions and commerce, whereas the fertile plains supported agriculture and the expansion of bigger city facilities. The regional variations in local weather and terrain have led to distinct regional cuisines, dialects, and cultural traditions. These regional variations are mirrored in the whole lot from native architectural kinds to conventional festivals and celebrations.
The nation’s geographic place has additionally influenced its relationship with different European nations and the broader world. Italy’s strategic location has made it a goal of invasion and conquest all through historical past, however it has additionally allowed it to play a major position in European politics and tradition. Its maritime traditions have related it to different Mediterranean cultures, leading to a wealthy cultural alternate.
Conclusion: Italy’s Enduring Legacy
A map of Europe is incomplete with out Italy, a nation whose distinctive geography has formed its historical past, tradition, and identification. The nation’s strategic location, its various landscapes, and its complicated regional variations have contributed to its wealthy tapestry of traditions and its enduring affect on European civilization. Understanding Italy’s geographical options is vital to appreciating its historic trajectory, its cultural variety, and its continued significance within the European context. From the snow-capped Alps to the sun-drenched Mediterranean coast, Italy’s geography is a strong narrative, woven into the material of its previous, current, and future. Additional exploration of particular areas, utilizing detailed maps and historic accounts, will solely deepen one’s appreciation of this fascinating and sophisticated nation.


/the-geography-of-italy-4020744-CS-5c3df74a46e0fb00018a8a3a.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/map-of-italy--150365156-59393b0d3df78c537b0d8aa6.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Navigating the Italian Peninsula: A Deep Dive into Italy’s Geography and its Place inside Europe. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!