Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Energy of Interactive Topographic Maps
Associated Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Energy of Interactive Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Energy of Interactive Topographic Maps. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Energy of Interactive Topographic Maps

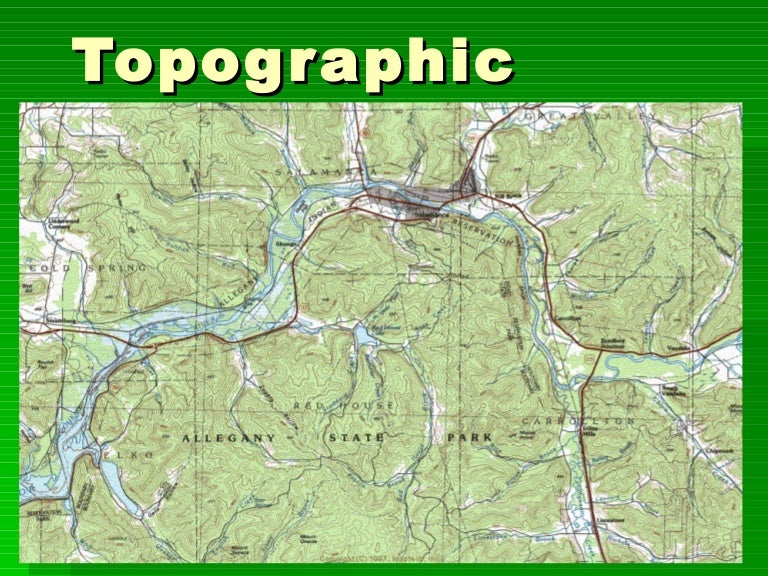
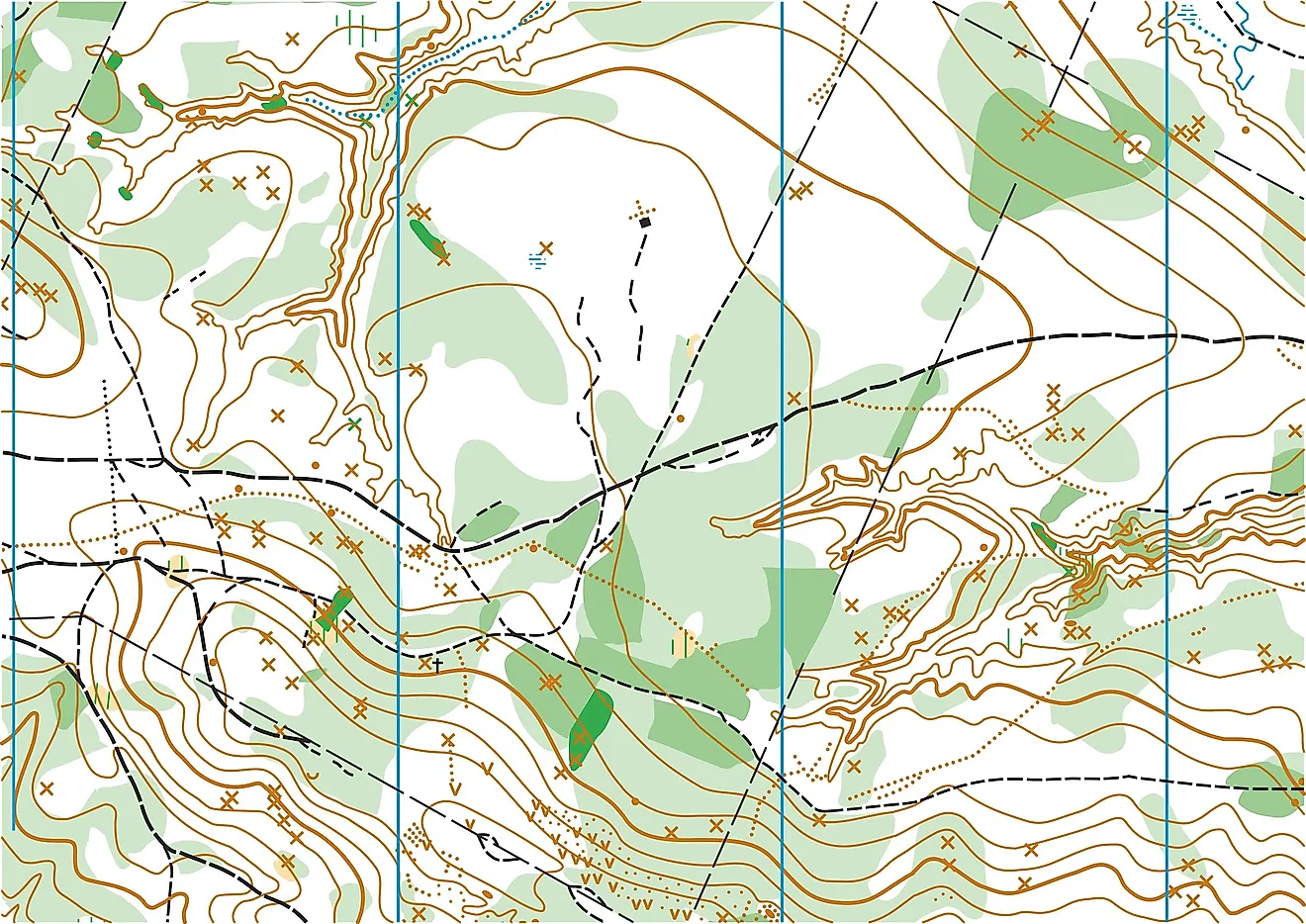
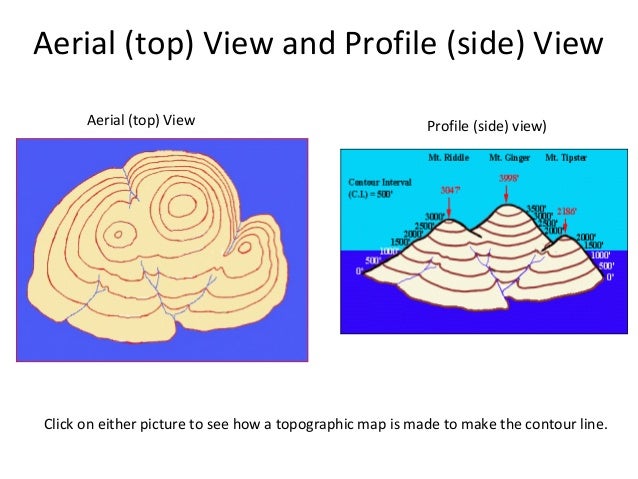
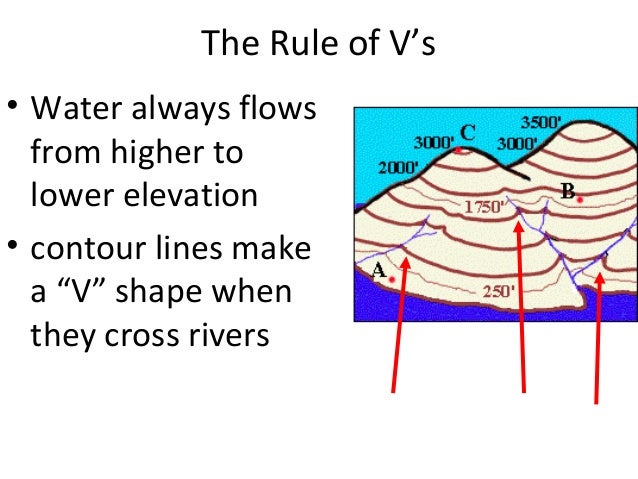
Topographic maps, with their contour strains depicting the rise and fall of the land, have lengthy been important instruments for geographers, hikers, engineers, and anybody needing an in depth illustration of the Earth’s floor. Nonetheless, static paper maps, whereas informative, have limitations. The appearance of interactive topographic maps has revolutionized how we perceive and work together with geographical knowledge, providing unprecedented ranges of element, accessibility, and analytical capabilities. This text explores the evolution, options, purposes, and future potential of those highly effective digital instruments.
From Static Strains to Dynamic Knowledge:
Conventional topographic maps, printed on paper, supplied a snapshot of a particular space’s elevation and options. Their limitations have been quite a few: lack of scalability, restricted capability to overlay different knowledge layers, and the lack to dynamically alter viewing views. The transition to digital codecs addressed these shortcomings. Early digital topographic maps have been basically digitized variations of their paper counterparts, providing improved storage and sharing capabilities. Nonetheless, the actual revolution got here with the combination of interactive components and the incorporation of superior knowledge visualization methods.
Trendy interactive topographic maps leverage the facility of Geographic Info Techniques (GIS) and net applied sciences to create dynamic and interesting experiences. They’re not simply static representations; they’re interactive platforms permitting customers to:
- Zoom and Pan: Seamlessly discover the map at numerous scales, from a broad overview to a extremely detailed view of a particular location.
- Rotate and Tilt: View the terrain from totally different angles, providing a extra immersive and intuitive understanding of the panorama.
- Overlay Knowledge: Combine a number of knowledge layers corresponding to roads, trails, factors of curiosity, satellite tv for pc imagery, and even real-time climate knowledge, offering a richer context for evaluation.
- Measure Distances and Areas: Precisely calculate distances between factors, perimeters of areas, and floor areas, essential for planning and evaluation.
- Create and Share Customized Maps: Generate customized maps with particular annotations, markers, and measurements, permitting for collaborative work and sharing.
- 3D Visualization: Expertise the terrain in three dimensions, providing a extra life like and intuitive understanding of elevation adjustments and spatial relationships.
Key Options of Superior Interactive Topographic Maps:
Past the fundamental functionalities, superior interactive topographic maps supply a spread of subtle options that improve their utility and analytical energy:
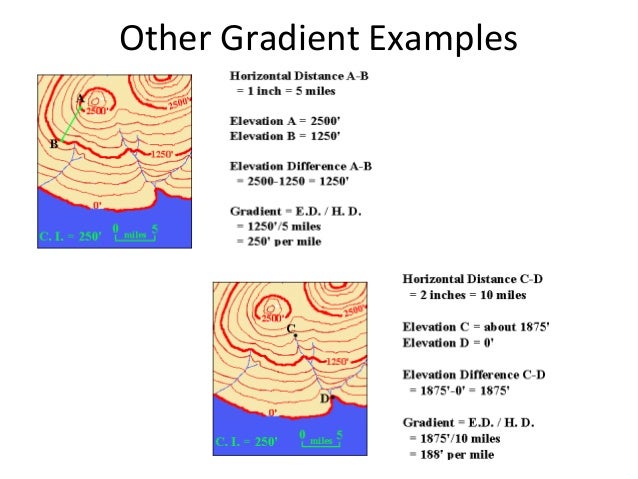
- Elevation Profiles: Generate cross-sectional profiles of the terrain alongside a user-defined line, revealing elevation adjustments and gradients. That is invaluable for planning mountain climbing routes, assessing street gradients, or understanding drainage patterns.
- Slope and Side Evaluation: Calculate and visualize slope angles and facet (path of slope), essential for understanding land stability, erosion potential, and photo voltaic radiation patterns.
- Watershed Delineation: Determine and visualize watersheds, essential for hydrological modeling, flood threat evaluation, and water useful resource administration.
- Line-of-Sight Evaluation: Decide visibility from a particular level, important for planning infrastructure, assessing visible influence, or figuring out potential vantage factors.
- Terrain Evaluation Instruments: Carry out superior spatial evaluation corresponding to interpolation, contouring, and floor modeling, permitting for detailed evaluation of landforms and their traits.
- Integration with different Knowledge Sources: Join with exterior databases and APIs to entry real-time knowledge corresponding to climate forecasts, visitors circumstances, or sensor readings, enriching the map’s context and utility.
Purposes Throughout Various Fields:
The flexibility of interactive topographic maps makes them indispensable throughout a variety of purposes:
- Outside Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and mountain bikers make the most of these maps for route planning, assessing path problem, and figuring out factors of curiosity. The flexibility to overlay path knowledge and elevation profiles is especially precious.
- City Planning and Improvement: Interactive maps support in website choice, infrastructure planning, and environmental influence assessments. The flexibility to overlay zoning laws, utility strains, and inhabitants density knowledge is essential.
- Civil Engineering and Building: Engineers use these maps for website surveying, street design, and building planning. The flexibility to carry out slope evaluation, line-of-sight evaluation, and quantity calculations is crucial.
- Environmental Administration: Ecologists and conservationists use them for habitat mapping, biodiversity evaluation, and monitoring environmental adjustments. The flexibility to overlay vegetation knowledge, wildlife sightings, and air pollution ranges is important.
- Emergency Response and Catastrophe Administration: Interactive maps present real-time situational consciousness throughout emergencies, facilitating environment friendly useful resource allocation and evacuation planning. The flexibility to overlay constructing footprints, street closures, and affected areas is essential.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Farmers and foresters use them for precision agriculture, crop administration, and forest stock. The flexibility to overlay soil kind knowledge, yield maps, and tree density is invaluable.
- Army and Protection: Interactive topographic maps are important for army operations, offering essential details about terrain, enemy positions, and potential routes. The flexibility to overlay real-time knowledge and carry out situational consciousness evaluation is crucial.
Technological Developments and Future Tendencies:
The sector of interactive topographic mapping is consistently evolving, pushed by developments in expertise and knowledge availability:
- Improved Knowledge Decision: Greater-resolution elevation knowledge from LiDAR and different distant sensing applied sciences is resulting in extra correct and detailed map representations.
- Enhanced 3D Visualization: Developments in 3D rendering methods are creating extra life like and immersive experiences, making it simpler to grasp advanced terrain.
- Integration with Augmented Actuality (AR): The combination of AR expertise permits customers to overlay digital map knowledge onto the actual world, offering a extra seamless and intuitive navigation expertise.
- Synthetic Intelligence (AI) and Machine Studying (ML): AI and ML are getting used to automate map creation, enhance knowledge accuracy, and improve analytical capabilities. For instance, AI can be utilized to robotically establish options corresponding to roads, buildings, and vegetation.
- Cloud-Based mostly Mapping Platforms: Cloud-based platforms supply larger scalability, accessibility, and collaborative capabilities, permitting a number of customers to entry and work with the identical map concurrently.
Challenges and Concerns:
Regardless of the quite a few benefits, some challenges stay:
- Knowledge Availability and Accuracy: The accuracy and availability of topographic knowledge fluctuate considerably throughout totally different areas of the world. In some areas, knowledge could also be outdated or incomplete.
- Knowledge Safety and Privateness: The gathering and use of geographical knowledge increase issues about privateness and safety. Strong knowledge safety measures are important to guard delicate info.
- Accessibility and Affordability: Entry to superior interactive topographic mapping instruments may be restricted by value and technical experience. Efforts are wanted to make these instruments extra accessible to a wider vary of customers.
Conclusion:
Interactive topographic maps have remodeled how we perceive and work together with the Earth’s floor. Their capability to seamlessly combine numerous knowledge layers, present dynamic visualization capabilities, and facilitate superior spatial evaluation has broadened their purposes throughout quite a few fields. As expertise continues to advance, these maps will turn out to be much more highly effective and accessible, additional enhancing our capability to navigate, perceive, and handle our planet’s advanced landscapes. The way forward for interactive topographic maps guarantees even larger element, seamless integration with different applied sciences, and a wider vary of analytical capabilities, solidifying their function as a necessary device for exploration, planning, and understanding our world.

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Navigating the Terrain: Exploring the Energy of Interactive Topographic Maps. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!